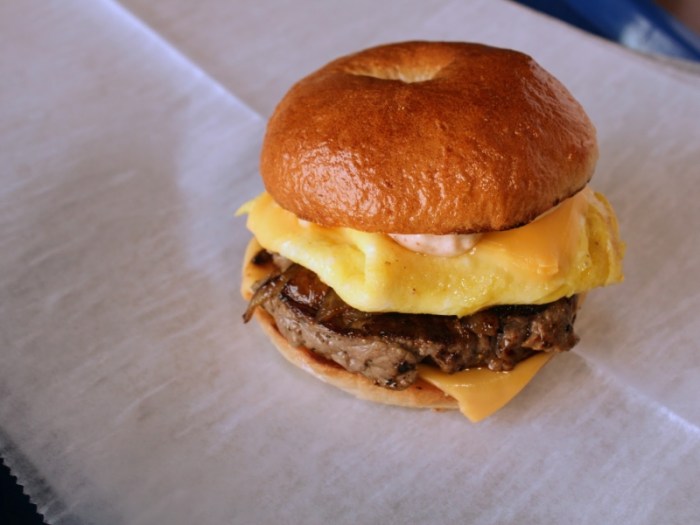
Kraft Cheese Nutritional Composition

Kraft cheese nutrition info – Let’s delve into the surprisingly nuanced world of Kraft cheese nutrition. While it might seem like a simple slice of processed cheese, a closer look reveals a surprisingly complex tapestry of macronutrients and micronutrients, each playing its part in the overall nutritional profile. Prepare to be amazed (or at least mildly intrigued).
Macronutrient Breakdown of Kraft Cheese Slices
A typical serving of Kraft Singles (one slice) offers a surprisingly balanced – or at least, balanced-ish – macronutrient profile. The exact amounts can vary slightly depending on the specific cheese variety, but generally, you’ll find a reasonable amount of protein to help you build and repair tissues, a decent helping of fat (mostly saturated, let’s be honest), and a surprisingly low carbohydrate count.
Think of it as a tiny, cheesy protein bar, but with significantly more sodium. For precise values, always refer to the nutritional information printed on the packaging. This is crucial, as even minor variations in cheese type can result in considerable differences in the macronutrient ratios.
Micronutrient Content of Kraft Cheese
Beyond the big three (protein, fat, carbs), Kraft cheese contributes a small but noticeable amount of various micronutrients. These essential vitamins and minerals are present in smaller quantities but still play vital roles in maintaining overall health. For example, Kraft cheese is a source of calcium, crucial for strong bones and teeth. It also contains small amounts of vitamins A and D, contributing to immune function and calcium absorption.
Again, the precise quantities vary depending on the type of cheese. The nutritional information panel on the packaging will always provide the most accurate data for the specific product. Always double-check, especially if you’re meticulously tracking your micronutrient intake.
Nutritional Profiles of Different Kraft Cheese Varieties
Kraft offers a variety of cheese slices, each with its own unique nutritional fingerprint. While the differences might seem subtle at first glance, they can add up over time. Let’s compare a few popular options:
| Cheese Type | Serving Size (slice) | Calories | Fat (g) | Protein (g) | Sodium (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sharp Cheddar | 1 slice | 70 | 6 | 6 | 220 |
| Colby | 1 slice | 70 | 6 | 6 | 210 |
| American | 1 slice | 60 | 5 | 5 | 190 |
*Note: These values are approximate and may vary depending on the specific product and packaging. Always check the nutrition label for the most accurate information.* The table clearly illustrates that even seemingly minor differences in cheese type can lead to variations in caloric content, fat, protein, and sodium levels. This highlights the importance of reading the nutrition label before consumption.
Remember, even small choices can add up!
Kraft Cheese and Dietary Considerations
Kraft cheese, that delightfully processed dairy delight, isn’t just a staple of childhood memories; it’s a nutritional entity deserving of a closer look, especially when considering various dietary needs. While undeniably convenient and tasty, understanding its place within a balanced diet requires a discerning eye, much like choosing the perfect cheese for a gourmet grilled cheese.Kraft cheese’s sodium content is a significant consideration for those watching their salt intake.
High sodium consumption can contribute to high blood pressure and other health issues. Therefore, individuals on low-sodium diets should carefully monitor their Kraft cheese consumption and perhaps opt for low-sodium varieties if available, or incorporate it sparingly into their meal plans. Remember, moderation is key – even with the most delicious things.
Kraft Cheese and Low-Sodium Diets
The sodium content in Kraft cheese varies depending on the specific product. Some varieties boast significantly lower sodium levels than others. For example, comparing a sharp cheddar to a reduced-sodium Colby Jack will reveal a considerable difference. Always check the nutrition label, as this information is crucial for informed dietary choices. A helpful strategy is to compare the sodium content per serving of Kraft cheese with other foods in your diet to maintain a balanced sodium intake.
Consider substituting Kraft cheese for lower-sodium alternatives in some meals to control overall sodium intake.
Understanding the nutritional composition of Kraft cheese involves examining its fat, protein, and sodium content. A comparative analysis often includes reviewing the nutritional profiles of other cheeses, such as a detailed examination of the feta cheese nutrition label , to highlight differences in macronutrient density. Returning to Kraft cheese, further investigation into its vitamin and mineral content provides a comprehensive nutritional assessment.
Comparison of Kraft Cheese with Other Processed Cheeses
Kraft cheese sits within a larger family of processed cheeses, each with its own nutritional profile. Comparing Kraft cheese to other brands reveals similarities and differences in fat, protein, and calcium content. For instance, some brands might emphasize reduced-fat options, while others focus on a higher protein content. The variations are subtle but exist, so comparing nutrition labels from different brands provides a more complete picture.
Consider factors such as the type of milk used (whole milk, skim milk), added ingredients, and processing methods when comparing nutritional content. This allows for a more informed decision based on individual dietary needs and preferences.
Impact of Kraft Cheese Consumption on Cholesterol Levels
Kraft cheese, like many dairy products, contains saturated fat, which can influence cholesterol levels. The amount of saturated fat varies across different Kraft cheese varieties. While some individuals may experience a slight increase in cholesterol levels with regular consumption, this effect is dependent on many factors including overall diet, individual metabolism, and pre-existing health conditions. A balanced diet that includes a variety of foods and limits overall saturated fat intake is recommended to manage cholesterol levels effectively.
Remember, it’s the overall dietary pattern, not just a single food, that largely dictates cholesterol impact. A single slice of Kraft cheese is unlikely to cause significant issues within a healthy dietary pattern.
Kraft Cheese and Health Claims
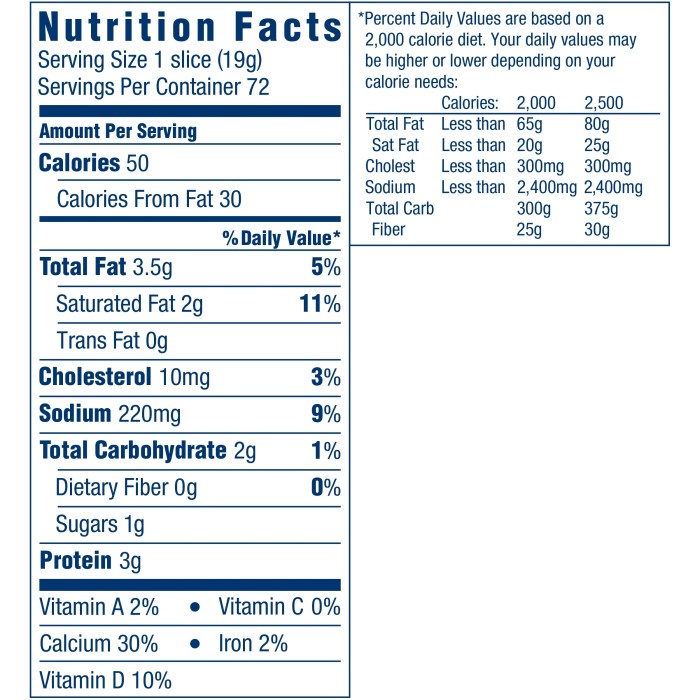
Kraft, like any purveyor of delicious dairy delights, treads carefully when it comes to making health claims about its cheese products. While they might not shout from the rooftops about miraculous health benefits, they do highlight certain nutritional aspects, often focusing on the protein and calcium content, which are undeniably present in significant amounts. However, the fun part lies in dissecting the science behind these implied claims and comparing them to the broader cheese landscape.
Let’s be clear: Kraft isn’t claiming its cheese will cure cancer or grant you eternal youth (though we wouldn’t rule it out entirely). Their marketing generally emphasizes the role of cheese in a balanced diet, often mentioning its contribution to calcium intake for strong bones. This is a claim supported by basic nutritional science – cheese is indeed a good source of calcium.
However, the context is crucial. While Kraft cheese provides calcium, excessive consumption can also contribute to high saturated fat and sodium intake, potentially offsetting any health benefits.
Calcium Content in Kraft Cheese
Kraft cheese, like most cheeses, contains a notable amount of calcium. This is a well-established fact, easily verified through nutritional information readily available on their packaging and website. However, the amount of calcium varies depending on the specific type of Kraft cheese. For instance, a slice of sharp cheddar will likely contain more calcium than a slice of processed cheese spread.
It’s important to remember that calcium is vital for bone health, but obtaining it solely from cheese might not be the most balanced approach, particularly considering other nutritional aspects. A balanced diet incorporating various calcium sources is generally recommended.
Saturated Fat and Sodium Content in Kraft Cheese Compared to Other Cheeses
| Cheese Type | Saturated Fat (per serving) | Sodium (per serving) | Potential Health Benefits | Potential Health Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kraft Singles | Relatively High | Relatively High | Convenient source of calcium and protein. | High saturated fat and sodium content may contribute to cardiovascular issues if consumed excessively. |
| Sharp Cheddar (Kraft or other brand) | High | Moderate to High | Good source of calcium and protein; may contain beneficial probiotics depending on production. | High saturated fat intake can negatively impact cholesterol levels. |
| Part-Skim Mozzarella | Lower than Cheddar | Moderate | Lower in fat than many cheeses; still a good calcium source. | May still contain significant sodium. |
| Feta Cheese | Moderate | Moderate | Good source of calcium and protein; often contains probiotics. | High sodium content is a concern for individuals with hypertension. |
The table above illustrates that while Kraft cheese contributes to calcium and protein intake, its saturated fat and sodium content can be a concern, particularly when compared to other cheese types. The health benefits and drawbacks are largely dependent on portion size and overall dietary habits. A single slice of Kraft cheese might not be a health catastrophe, but consistent consumption of large quantities warrants consideration of the potential negative impacts.
Visual Representation of Nutritional Information: Kraft Cheese Nutrition Info

A picture, as they say, is worth a thousand calories – or at least a thousand words when it comes to understanding the nutritional breakdown of Kraft cheese. Visual aids can make deciphering nutritional labels far more palatable than staring at a dense table of numbers. Let’s explore how we can visually represent the nutritional data in a way that’s both informative and, dare we say, entertaining.
Macronutrient Composition Pie Chart
Imagine a vibrant pie chart, a delicious-looking representation of Kraft cheese’s macronutrient profile. Each slice represents a different macronutrient – fat, protein, and carbohydrates – sized proportionally to its contribution to the total calories. For instance, a larger slice might represent the fat content (given Kraft cheese’s nature), a moderately sized slice would show the protein, and a smaller slice, perhaps surprisingly small, would represent carbohydrates.
The colours used could be strategically chosen to enhance visual appeal; perhaps a creamy yellow for fat, a robust brown for protein, and a gentle beige for carbohydrates. Clear labels would identify each slice and its corresponding percentage of the total calories. This visual would instantly convey the relative proportions of each macronutrient, allowing for quick and easy comprehension.
Sodium Content Comparison Bar Graph, Kraft cheese nutrition info
To illustrate the sodium content of Kraft cheese relative to the recommended daily intake, a simple bar graph is ideal. One bar would represent the sodium content in a standard serving of Kraft cheese (clearly labelled, of course). A second, taller bar would represent the recommended daily intake of sodium according to established dietary guidelines (e.g., the American Heart Association’s recommendation).
The difference in bar height would instantly highlight the proportion of the recommended daily intake contained in a single serving of Kraft cheese. Using contrasting colours – perhaps a bright orange for the Kraft cheese sodium and a calming blue for the recommended intake – would make the comparison even more striking. A clear title and labels would ensure the information is easily understood.
This visual would allow consumers to easily assess the sodium content within the context of their overall daily intake, promoting informed dietary choices. For added impact, the percentage of the recommended daily intake represented by the Kraft cheese serving could be displayed prominently on the graph.
General Inquiries
Is Kraft cheese good for weight loss?
Kraft cheese can be part of a weight-loss diet in moderation, but it’s higher in fat and sodium than some other cheese options. Choose lower-fat varieties and watch your portion sizes.
Does Kraft cheese contain lactose?
Most Kraft cheese varieties contain lactose, although some may offer lactose-reduced options. Always check the label.
Can I eat Kraft cheese if I’m pregnant?
Yes, but as with any food during pregnancy, moderation is key. Pay attention to the sodium content and ensure you’re consuming a balanced diet.
Are there vegetarian/vegan Kraft cheese alternatives?
Kraft itself doesn’t offer vegan cheese, but many other brands provide delicious alternatives. Check your local grocery store!






