Nutritional Composition of Sharp Cheddar Cheese: Sharp Cheddar Cheese Nutrition Facts
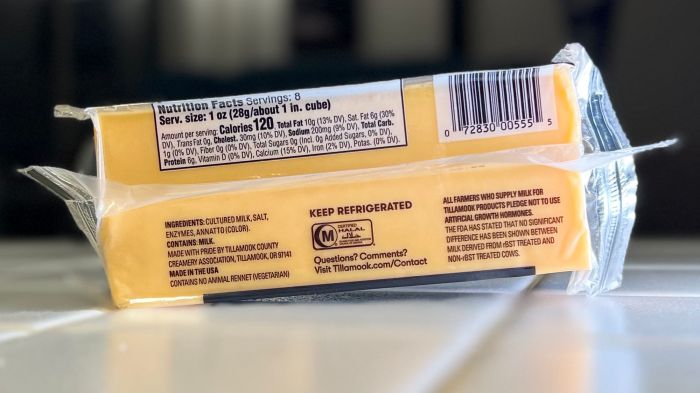
Sharp cheddar cheese nutrition facts – Sharp cheddar cheese, a popular dairy product, offers a significant source of various nutrients. Understanding its nutritional profile is crucial for informed dietary choices, considering its role in contributing to both beneficial and potentially detrimental aspects of overall health. This section details the macronutrient and micronutrient composition of a typical serving, along with an analysis of its fat content.
Macronutrient Composition of Sharp Cheddar Cheese
The following table presents a breakdown of the macronutrients in a standard 1-ounce (approximately 28-gram) serving of sharp cheddar cheese. Values may vary slightly depending on the specific brand and production methods.
| Nutrient | Amount per serving (grams) | % Daily Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fat | 8-9 | 12-14% | Primarily saturated fat, with smaller amounts of unsaturated fats. |
| Protein | 7-8 | 14-16% | Provides essential amino acids. |
| Carbohydrates | 1 | <1% | Primarily lactose. |
Micronutrient Content of Sharp Cheddar Cheese
Sharp cheddar cheese is a good source of several essential micronutrients, contributing to overall health and well-being. These nutrients play vital roles in various bodily functions.
Sharp cheddar cheese is a notably good source of the following vitamins and minerals:
- Vitamin A: Contributes to vision, immune function, and cell growth.
- Vitamin D: Crucial for calcium absorption and bone health. The amount varies depending on whether the cheese is made with milk from cows exposed to sunlight.
- Vitamin K2: Important for bone health and cardiovascular function.
- Vitamin B12: Essential for nerve function and red blood cell formation.
- Calcium: Essential for strong bones and teeth.
- Phosphorus: Works with calcium for bone health and various other bodily functions.
- Zinc: Supports immune function and wound healing.
Saturated and Unsaturated Fat Content and Health Implications
Sharp cheddar cheese contains a relatively high proportion of saturated fat. While saturated fats have been associated with increased LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels and potential cardiovascular risks in some studies, the impact of dietary saturated fat remains a subject of ongoing research and debate. The cheese also contains smaller amounts of unsaturated fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are generally considered beneficial for heart health.
Understanding sharp cheddar cheese nutrition facts is crucial for mindful eating. A single slice packs a decent amount of protein and calcium, but the fat content can add up quickly. Consider this when comparing it to the total fat and calorie count in a breakfast favorite, like the sausage egg and cheese mcmuffin nutrition , which often features cheddar.
Ultimately, balancing your sharp cheddar intake with your overall dietary choices is key to a healthy lifestyle.
Moderation in consumption is advised, considering individual dietary needs and health status. It’s important to note that the overall dietary pattern, including other food choices and lifestyle factors, significantly impacts cardiovascular health. Therefore, the effects of sharp cheddar cheese’s fat content should be considered within the context of a balanced diet.
Sharp Cheddar Cheese and Dietary Considerations
Sharp cheddar cheese, while a flavorful and popular dairy product, presents a unique nutritional profile that necessitates careful consideration within various dietary contexts. Understanding its composition relative to other cheeses and its implications for specific dietary plans is crucial for informed consumption.
Nutritional Comparison of Cheeses
The following table compares the nutritional profile of sharp cheddar cheese with that of Colby and Monterey Jack cheeses, highlighting key differences in fat, protein, and calcium content. These values are approximate and can vary based on factors such as milk source and processing methods.
| Cheese Type | Fat Content (g/100g) | Protein Content (g/100g) | Calcium Content (mg/100g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sharp Cheddar | 33-35 | 25-28 | 700-800 |
| Colby | 28-30 | 24-26 | 650-750 |
| Monterey Jack | 25-27 | 22-24 | 600-700 |
Sharp Cheddar Cheese in Various Diets, Sharp cheddar cheese nutrition facts
Sharp cheddar cheese’s nutritional composition influences its suitability for different dietary approaches.
The following points Artikel the role of sharp cheddar cheese in various dietary plans:
- Ketogenic Diets: Sharp cheddar cheese, being relatively high in fat and low in carbohydrates, can be incorporated into ketogenic diets. However, portion control is essential to maintain ketosis, as even small amounts of carbohydrates can impact blood sugar levels. For example, a 1-ounce serving of sharp cheddar contains approximately 1 gram of carbohydrate.
- Low-Carb Diets: Similar to ketogenic diets, sharp cheddar cheese fits into low-carbohydrate plans due to its low carbohydrate content. It provides satiety and protein, contributing to weight management goals. However, individuals should monitor their overall carbohydrate intake to remain within their dietary limits.
- High-Protein Diets: Sharp cheddar cheese offers a significant amount of protein, contributing to the protein requirements of high-protein diets. It can be a convenient source of protein for individuals aiming to increase their protein intake, such as athletes or those focused on muscle building. However, high fat content needs to be considered within the context of overall dietary fat limits.
Allergens in Sharp Cheddar Cheese and Dietary Restrictions
Sharp cheddar cheese, like other dairy products, contains milk proteins which are a common allergen. Individuals with milk allergies must strictly avoid consuming sharp cheddar cheese, as even trace amounts can trigger allergic reactions ranging from mild discomfort to severe anaphylaxis. Lactose intolerance, while not a true allergy, can also cause digestive distress in individuals who lack the enzyme lactase to digest lactose, a sugar present in milk.
Product labels should be carefully examined for allergen information, and individuals with dietary restrictions should consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians to determine appropriate dietary choices.
User Queries
Is sharp cheddar cheese good for weight loss?
Sharp cheddar is high in fat and calories, making it less ideal for weight loss compared to lower-fat cheese options. Portion control is essential.
Can vegetarians eat sharp cheddar cheese?
Yes, most sharp cheddar cheese is vegetarian-friendly, but always check the label to ensure it doesn’t contain animal rennet.
Does sharp cheddar cheese contain lactose?
Yes, sharp cheddar cheese contains lactose, though aging reduces the amount. Individuals with lactose intolerance may experience varying degrees of discomfort.
How does aging affect the nutritional content of sharp cheddar?
Aging can slightly alter the nutritional content, often reducing moisture and lactose while concentrating flavor and some nutrients.






